Cover Photo by Avery Evans on Unsplash
Business across all sectors, from retail to banking, rely on relational databases to extract competitive insights. However, due to the privacy regulations set in place to protect individuals’ data, the available information is currently locked into data silos.
In today's digital age, businesses and organizations rely heavily on Relational Databases for storing valuable information. From Oracle databases to Microsoft SQL servers and Snowflake's modern Data Warehouse solution, these databases hold a wealth of data. However, with the increasing importance of privacy regulations, it is crucial to have privacy-enhancing technologies that can seamlessly integrate with these databases and meet their structural requirements. This ensures not only proper data management but also fast and secure access to the information stored within.
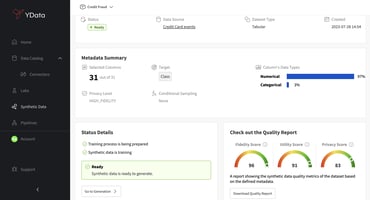
Fabric offers a cutting-edge Synthetic data generation process that seamlessly integrates with your existing Relational databases. By replicating the data's value and structure to a new target storage, Fabric delivers a wide range of benefits and use-cases. These include reducing risk and improving compliance by substituting operational databases with synthetic databases for tests and development. It also enables QA teams to create comprehensive and more flexible testing scenarios. Additionally, synthetic data can be used to augment available data volumes effortlessly, making it ideal for performance testing. With just a few clicks, Fabric empowers businesses with a powerful tool for data management and analysis.
Discover how Fabric can revolutionize your data management by effortlessly generating Synthetic Relational databases that offer a secure, efficient, and authentic alternative to using real operational data. Unlock the power of your data with synthetic data and gain valuable insights.
Download our case study now to learn more about:
- Synthetic Relational databases data benefits
- How to generate synthetic relational datasets
- The quality & privacy guarantees of the generated synthetic data